# Git
- GitHub (opens new window)
- Website (opens new window)
- Website (opens new window)
- 《Git权威指南》
- git - 简明指南 (opens new window)
- learnGitBranching (opens new window)
TIP
- Worksapce: 工作区
- Index/Stage: 暂存区
- Repository: 本地仓库
- Remote: 远程仓库
HEAD: 始终指向当前所处分支的最新的提交点,实质上是一个指针,指向最新放入仓库的版本。
# Tig
text-mode interface for Git
# .git
-rw-r--r-- 1 squirrel staff 9 12 18 23:59 COMMIT_EDITMSG
-rw-r--r-- 1 squirrel staff 21 12 19 17:44 HEAD
-rw-r--r-- 1 squirrel staff 41 12 18 23:49 ORIG_HEAD
-rw-r--r-- 1 squirrel staff 137 12 18 23:19 config
-rw-r--r-- 1 squirrel staff 73 12 18 23:19 description
drwxr-xr-x 15 squirrel staff 480 12 18 23:19 hooks
-rw-r--r-- 1 squirrel staff 554 12 19 01:26 index
drwxr-xr-x 3 squirrel staff 96 12 18 23:19 info
drwxr-xr-x 4 squirrel staff 128 12 18 23:35 logs
drwxr-xr-x 25 squirrel staff 800 12 18 23:59 objects
drwxr-xr-x 4 squirrel staff 128 12 18 23:19 refs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# config
config 的三个作用域
- git config --local: local 只对当前仓库有效
- git cinfig --global: global 对当前用户所有仓库有效
- git config --system: system 对系统所有登录的用户有效
# 查看所有列表
git config --list
git config --list --local
git config --list --global
git config --list --system
# 查看指定属性的值
git config --global user.name
git config --global user.email
# 修改指定属性的值
git config --global user.name 'squirrel'
git config --global user.email 'squirrel@gmail.com'
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# HEAD
指向 refs/heads
# detached HEAD
分离头指针:比如在执行 git checkout <commitId> 时会出现分离头指针,这种情况下比较危险,因为此时提交的代码没有对应的分支,当切换到其他分支后,可能会被 git 清理导致丢失代码。
分离头指针应用场景:
- 如果临时想基于某个 commit 做变更,试试新方案是否可行,就可以采用分离头指针的方式。测试后发现新方案不成熟,直接 reset 回其他分支即可,省却了建、删分支的麻烦;如果觉得有用,那么可以新建一个分支,使用
git branch <新分支名称> <在分离头指针上提交的 commitId> - git rebase工作的过程中,就是用了分离头指针。rebase意味着基于新base的commit来变更部分commits。它处理的时候,把HEAD指向base的commit,此时如果该commit没有对应branch,就处于分离头指针的状态,然后重新一个一个生成新的commit,当rebase创建完最后一个commit后,结束分离头状态,Git让变完基的分支名指向HEAD。
# refs
- heads
- tags
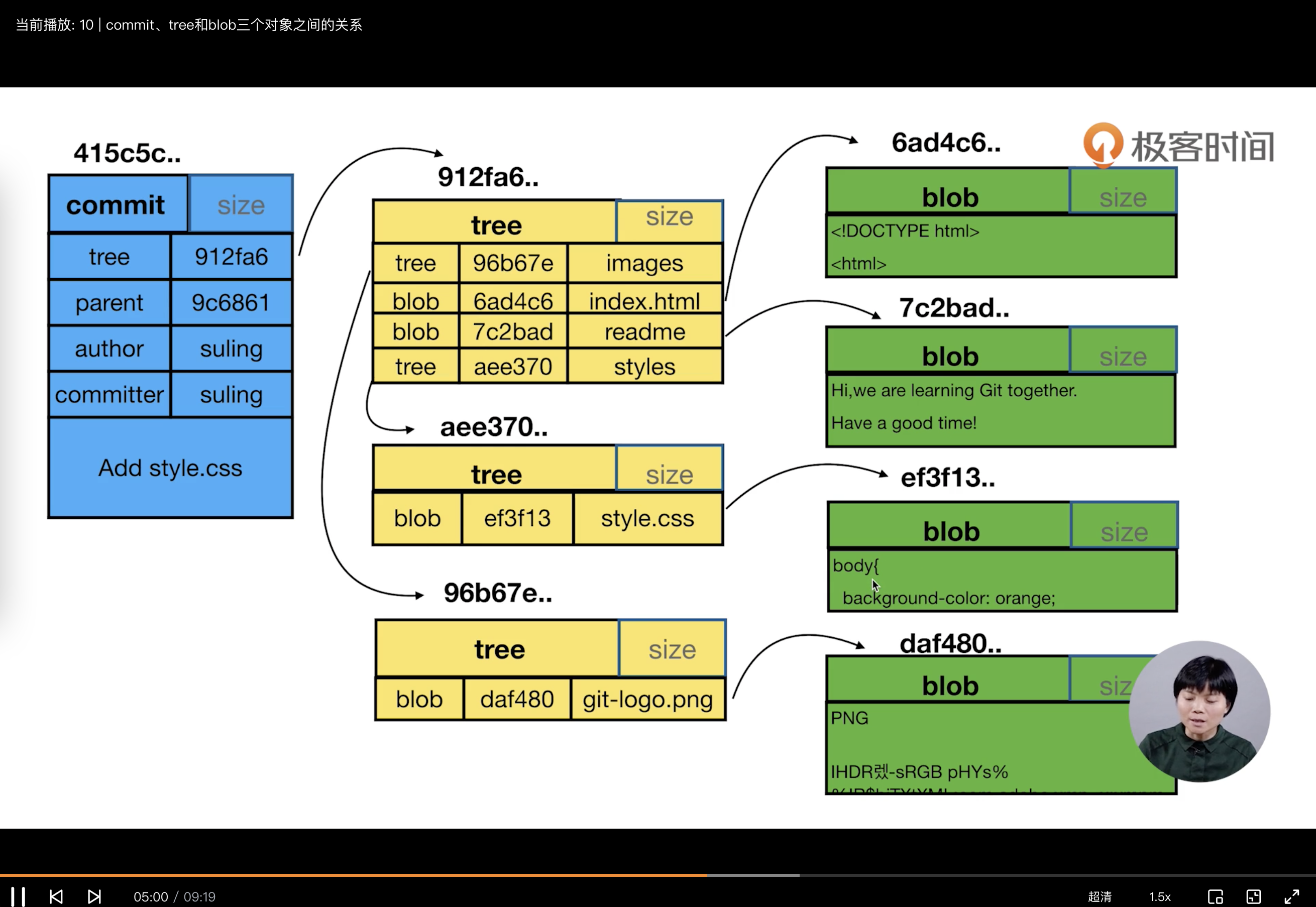
# objects
可以通过git cat-file查看对象
# 查看 git 对象的类型,可能为 commit tree blob tag
git cat-file -t c1b64e40e5cab82f5e20dd83b1aa8c00ab4606e7
# 查看 git 对象的内容
git cat-file -p c1b64e40e5cab82f5e20dd83b1aa8c00ab4606e7
# 查看 git 对象的大小
git cat-file -s c1b64e40e5cab82f5e20dd83b1aa8c00ab4606e7
# 显示暂存区所有文件对应的属性,包括blob的hash值
git ls-files --stage
find .git/objects -type f
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 命令
# init
git init: 在当前目录新建一个 git 代码库git init [<directory>]: 将目录(不存在时先新建)初始化为一个 git 代码库
# clone
常用的传输协议
| 传输协议 | 语法格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 本地协议(1) | /path/to/repo.git | 哑协议 |
| 本地协议(2) | file:///path/to/repo.git | 智能协议 |
| http/https 协议 | http://git-server.com:port/path/to/repo.git https://git-server.com:port/path/to/repo.git | 平时接触到的都是智能协议(用户名密码) |
| ssh 协议 | user@git-server.com:path/to/repo.git | 工作中最常用的智能协议(公私钥) |
哑协议与智能协议
- 直观区别:哑协议传输进度不可见;智能协议传输进度可见
- 传输速度:智能协议比哑协议传输速度快
# git clone --bare 创建裸仓库,不包含工作区,可作为远端备份
# http://www.worldhello.net/gotgit/02-git-solo/100-git-clone.html#id4
git clone --bare /Users/squirrel/practice/git-demo/.git ya.git
# 把裸仓库变为普通仓库
mkdir ya
mv ya.git ya
cd ya
mv ya.git .git
git config core.bare false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# remote
man git-remote
git help remote
git help remote --web
git remote --help
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
git remote -v: 显示远程仓库- git remote show [remote]: 显示指定远程仓库信息
git remote add <origin name> <server URL>: 将本地仓库连接到指定远程服务器- git remote add [shortname] [url]: 增加一个新的远程仓库,并命名
- git remote update: 更新远程仓库
- git pull [remote] [branch]: 拉取远程仓库的变化,并与本地分支合并
- git push [remote] [branch]: 推送本地分支到远程仓库
- git push [remote] --force: 强行推送当前分支到远程仓库
- git push [remote] --all: 推送所有分支到远程仓库
# add
git add <file | directory>: 添加工作区的指定目录或文件到暂存区git add *.html: 添加工作区的指定类型文件(使用通配符方式批量提交)到暂存区git add -u: 添加已经被add的文件且存在更改的文件(Git根路径以下所有文件)到暂存区(提交被修改(modified)和被删除(deleted)文件,不包括新文件(new))git add .: 添加工作区当前目录下的所有存在更改文件到暂存区(包括提交新文件(new)和被修改(modified)文件,不包括被删除(deleted)文件)git add --all: (简写为git add -A)添加所有变化(Git根路径以下所有文件)到暂存区(包括提交新文件(new)、被修改(modified)文件以及被删除(deleted)文件)
# commit
git commit -m <message>: 提交暂存区到仓库区git commit [file1 [file2...]] -m <message>: 提交暂存区的指定文件到仓库区git commit -a: 提交工作区自上次commit之后的变化,直接到仓库区git commit -v: 提交时显示所有的diff信息git commit --amend: 修改最近一次的提交的 message- 注意:用于未 push 之前
- 已经 push 到远端的话,得用 push -f 了
git commit --amend -m <message>: 使用一次新的commit,替代上一次提交,如果代码没有任何变化,则用来改写上一次commit的提交信息git commit --amend [file1 [file2...]]: 修改上一次commit,并包括指定文件的新变化
TIP
commit 规范
# branch
man git-branch
git help branch
git help branch --web
git branch --help
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
git branch [-v]: 查看本地分支git branch -r: 查看远程分支git branch -a: 查看本地分支和远程分支git branch <new-branch>: 【以当前分支为基础】新建分支,但依然停留在当前分支git branch <new-branch> <commit>: 以指定的提交为基础,新建分支,但依然停留在当前分支git branch -d <branch>: 删除本地分支git branch -D <branch>: 强制删除本地分支git branch -dr <remote-branch>: 删除远程分支git branch --track <remote-branch> <branch>: 新建分支,并与指定远程分支建立追踪关系git branch --set-upstream-to <remote-branch> <branch>: 将现有的指定分支与远程分支建立追踪关系git checkout -: 切换到上一分支git checkout <branch>: 切换到指定分支,并更新工作区git checkout -b <new-branch>: 【以当前分支为基础】新建分支(分支名为 new-branch),并切换到新建的分支git checkout -b <new-branch> <branch>: 以指定的分支(分支名为 branch)为基础,新建分支,并切换到新建的分支git checkout -b <new-branch> <commit>: 以指定的提交为基础,新建分支,并切换到新建的分支git merge <branch>: 合并指定分支到当前分支git cherry-pick <commit>: 选择一个commit,合并进当前分支
# log
man git-log
git help log
git help log --web
git log --help
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
git log: 查看当前分支的提交历史git log <branch>: 查看指定分支的提交历史git log --all: 查看所有分支的提交历史git log -n4: 查看最近4条git log -p: 查看每个commit的具体改动git log --stat: 查看每次更新的修改文件的统计信息git log --shortstat: 只显示--stat中最后的行数添加修改删除统计git log --name-only: 只在已修改的提交信息后显示文件清单git log --name-status: 显示新增、修改和删除的文件清单git log --graph: 使用ASCII艺术的树形结构来展示分支git log --abbrev-commit: 仅显示SHA-1的前几个字符,而非所有的40个字符git log --oneline: (git log --pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit的简写)每一条提交记录只占一行git log --pretty=[oneline, short, medium, full, fuller, reference, email, raw, format:<string>]: 每一条提交记录只占一行git log --date=<default, iso8601, local, relative, short, format:, iso8601-strict, raw, rfc2822, unix>: 修改时间格式git log --relative-date: (与git log --date=relative同义)使用相对时间显示git show: 查看最新commit的改动git show <commit>: 查看指定commit的改动
git log --all --color --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset'
1
(stackoverflow) Can I get git to tell me all the files one user has modified? (opens new window)
git log --pretty="%H" --author="yusong zhou" | while read commit_hash; do git show --oneline --name-only $commit_hash | tail -n+2; done | sort | uniq
git log develop --pretty="%H" --committer="yusong zhou" --after="2021-12-01" --before="2021-12-31" | while read commit_hash; do git show --oneline --name-only $commit_hash | tail -n+2; done | sort | uniq
1
2
3
2
3
# rebase
- 修改 commit message:
git rebase -i <parent_commit>reword- 注意:用于未 push 到公共分支之前(只要不影响到其他同事的分支,都可以自行整理,公共的分支坚决不行,不然会给他人带去及其不必要的痛苦)
- 修改第一次提交的 message (opens new window):
git rebase -i --root
- 合并 commit:
git rebase -i <parent_commit>squash
# diff
man git-diff
git help diff
git help diff --web
git diff --help
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
git diff [-- file1 [file2...]]: 工作区和暂存区的差异git diff --cached [-- file1 [file2...]]: 暂存区和 HEAD 的差异git diff --staged [-- file1 [file2...]]: 暂存区和 HEAD 的差异git diff HEAD [-- file1 [file2...]]: 工作区和 HEAD 的差异git diff <commit1> <commit2> [-- file1 [file2...]]: commit1 和 commit2 这两次提交的差异
git diff HEAD^ HEAD
git diff HEAD^1 HEAD
git diff HEAD^^ HEAD
git diff HEAD~ HEAD
git diff HEAD~1 HEAD
git diff HEAD~2 HEAD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
TIP
PARENT 符号 ^ 和 ~
- 一个节点,可以包含多个子节点(checkout 出多个分支)
- 一个节点可以有多个父节点(多个分支合并)
- ^是~都是父节点,区别是跟随数字时候,^2 是第二个父节点,而~2是父节点的父节点
- ^和~可以组合使用,例如 HEAD~2^2
参考: git在回退版本时HEAD~和HEAD^的作用和区别 (opens new window) stackoverflow What's the difference between HEAD^ and HEAD~ in Git? (opens new window)
# stash
man git-stash
git help stash
git help stash --web
git stash --help
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
git stash [push [-m|--message <message>]]: 储藏git stash save [<message>]: 储藏git stash list: 查看现有的储藏git stash show -p [stash@{0}]: 查看储藏内容git stash apply [stash@{0}]: 应用储藏(不会删除该储藏内容)git stash drop [stash@{0}]: 删除储藏内容git stash pop [stash@{0}]: 应用储藏(会删除该储藏内容)git stash branch <branch>: 从储藏中创建分支,检出你储藏工作时的所处的提交,重新应用你的工作,如果成功,将会丢弃储藏。
# 撤销
# checkout 恢复工作区
git checkout -- <file>: 使用 HEAD 中的最新内容替换掉你的工作目录中的文件,已添加到暂存区的改动以及新文件都不会受到影响。- Git 2.23 之后,用
git switch <new-branch>替换切换分支的功能,git restore <file>替换对工作区文件进行恢复的功能。
- Git 2.23 之后,用
git checkout [commit] [file]: 恢复暂存区的指定文件到工作区
# reset 恢复暂存区
man git-reset
git help reset
git help reset --web
git reset --help
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
git reset HEAD [-- file [file...]]: 让暂存区恢复成和 HEAD 一样git reset --hard [<commit>]: 清空工作区和暂存区中的修改git reset --hard HEAD^: 清空工作区和暂存区中的修改
WARNING
git reset --hard 注意事项
当我们 git reset --hard 操作进行了版本回退,现在又需要之前的修改信息,也就是说我们需要版本回退之前的文件信息,此时分为三种情况:
- 之前的修改没有进行
git add,目前无能为力不能恢复 - 之前的修改进行了
git add但没有git commit,这种情况还可以抢救。- 第一步:
git fsck --lost-found - 第二步:
git show [blob] > 文件
- 第一步:
- 之前的修改进行了
commit提交,这种最简单,执行git reflog拿到哈希值后再git reset即可
# 重命名文件
git mv <source file> <destination file>
# 删除文件/目录
git rm <file>git rm -r <directory>
# .gitignore
- github/gitignore (opens new window)
- 忽略已提交的文件: (opens new window)
- 把想忽略的文件添加到 .gitignore
git rm --cached <file>
# 参考链接
- https://juejin.im/post/5af0438f5188251b8015967e (opens new window)
- https://juejin.im/post/5ce4ddb351882532e9631951 (opens new window)
- http://gitready.com/advanced/2009/01/17/restoring-lost-commits.html (opens new window)
- http://www.programblings.com/2008/06/07/the-illustrated-guide-to-recovering-lost-commits-with-git/ (opens new window)
- https://github.com/521xueweihan/git-tips (opens new window)
Linux →